So-called electromagnetic interference, in a broad sense, all non-useful signals entering the channel or communication system are called electromagnetic interference. Electromagnetic interference has penetrated into our daily lives. For example, when watching TV, some people nearby use electric drills, hair dryers and other electrical appliances, which will make the TV screen appear snowy, the sound of the sound in the sounder... and so on. People of this type have long been commonplace and used to it, but the harm of electromagnetic interference is far more than that. In fact, electromagnetic interference has caused civil aviation system failure, poor communication, computer operation errors, malfunction of self-controlled equipment, and even endangering personal safety. Therefore, how to effectively suppress electromagnetic interference has become a factor that analog engineers must have and consider. Here, we will detail what electromagnetic interference is and how to effectively suppress electromagnetic interference.
Analysis of electronic circuits and electromagnetic interference
Modern electronic products are becoming more and more powerful, and electronic circuits are becoming more and more complex. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic compatibility issues have become major problems, and circuit design has become more and more demanding for designers. Electromagnetic interference is generally divided into two types, conducted interference and radiated interference. Conducted interference refers to the coupling (interference) of signals on one electrical network to another electrical network through a conductive medium. Radiated interference refers to an interference source that couples (interferes) its signal to another electrical network through space. Therefore, the research on EMC problem is the study of the relationship between interference source, coupling path and sensitive equipment.
In 1990, the US Federal Communications Commission introduced regulations on commercial digital products in 1992, which required companies to ensure that their products meet strict susceptibility and emission criteria. Products that comply with these regulations are said to be electromagnetically compatible.
At present, EMC has basically set up corresponding market access certifications in various regions of the world to protect the electromagnetic environment of the region and the competitive advantages of local products. Such as: North American FCC, NEBC certification, EU CE certification, Japan's VCCEI certification, Australia's C-TIck certificate, Taiwan's BSMI certification, China's 3C certification are all "passports" to enter these markets.
Electromagnetic induction and electromagnetic interference
Many people are engaged in the design of electronic circuits, starting with the understanding of electronic components, but the electromagnetic compatibility design should actually start from the electromagnetic field theory, that is, from the electromagnetic induction.
The general electronic circuit is composed of resistors, capacitors, inductors, transformers, active devices and wires. When there is voltage in the circuit, an electric field is generated around all the charged components. When there is current flowing in the circuit. At the time, there is a magnetic field around all the carrier fluids.
The capacitor is the most concentrated component of the electric field. The current flowing through the capacitor is the displacement current. This displacement current is caused by the two plates of the capacitor being charged and generating an electric field between the two plates. Charge and discharge are generated to form a displacement current. In fact, the current in the capacitor circuit does not actually flow through the capacitor, but only charges and discharges the capacitor. When the two plates of the capacitor are opened, the two plates can be regarded as a set of electric field radiating antennas, and the circuit between the two plates will induce an electric field between the plates. The circuit between the two plates, whether it is a closed loop or an open circuit, generates a displacement current in the conductor that is in the same direction as the electric field (when the direction of the electric field changes constantly), that is, the current runs forward for a while, and then runs backward.
The electric field strength is defined as the potential gradient, that is, the ratio of the potential difference to the distance between two points. A wire that is several meters long, when it flows through a few amperes of current, the voltage across it is at most a few tenths of volts, that is, the electric field strength of several tens of millivolts per meter, which can generate several amps of current in the conductor. It can be seen that the electric field has a great effect and its interference ability is strong.
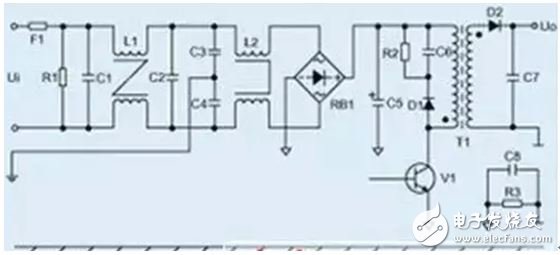
Inductors and transformers are the most concentrated components of the magnetic field. The current flowing through the secondary winding of the transformer is the induced current. This induced current is generated by magnetic induction when a current flows through the primary coil of the transformer. The circuit around the inductor and the transformer can be regarded as an induction coil of a transformer. When the magnetic flux generated by the leakage inductance of the inductor and the transformer passes through a certain circuit, the circuit acts as a "secondary coil" of the transformer. Induced current. The circuit of two adjacent loops can also regard one of the loops as the "primary coil" of the transformer, and the other loop can be regarded as the "secondary coil" of the transformer, so two adjacent loops are also produced. Electromagnetic induction, that is, mutual interference.
As long as an electric field or a magnetic field exists in the electronic circuit, electromagnetic interference occurs. In high-speed PCB and system design, high-frequency signal lines, integrated circuit pins, various types of connectors, etc. may become radiation interference sources with antenna characteristics, can emit electromagnetic waves and affect other systems or other subsystems in the system. normal work.
Classification of electromagnetic interference
Specific to "electromagnetic interference", it can be divided according to the seven categories listed below:
According to the source of the division
According to the propagation path
According to the cause of radiation interference
According to the working principle of different devices
Divided by frequency of occurrence
Divided by frequency range
Different AC power supplies
Lawn lamp design mainly exterior and downy lamplight add security for urban green space landscape and beautiful, and generally has the characteristic such as easy installation, adornment sex is strong, can be used for park, garden villas, square, greening, greening of the place such as decorative lighting.

Product features
1. The lamp body is made of aluminum alloy with the column in high strength
2. Static powder spray coating process with many different colors for options
3. The LED lighting modules give the highest lighting output to produce the optiumum light beam control and visual comfort.
4. Protection:IP54
5. Heart radiation structure design for lighting assembly,greatly enhancing the stability and lifespan of the lamp.
6. LED Lighting columns with RGB and change program comprising artistic design elements.
7. Reasonable design for assembling and disassembling,convenient for installation and maintenance.
Lawn Lamps,Solar Lawn Lamps,Outdoor Lawn Lamps,Gas Lawn Lamps
Jiangsu chengxu Electric Group Co., Ltd , https://www.chengxulighting.com
