High Resistance State
In digital circuits, the high-resistance state is a common term that refers to an output condition that is neither high nor low. This state is often referred to as the high-impedance state. When a high-impedance signal is fed into the next level of a circuit, it essentially means there's no active connection. If measured with a multimeter, it might show either a high or low level, depending on what’s connected downstream.
The essence of a high-impedance state can be understood as an open circuit. It represents a situation where the output (or input) has a very high resistance, effectively disconnecting it from the rest of the circuit. In theory, this state isn't completely floating; it's more like a state of high resistance relative to ground or power. In practice, it behaves similarly to a floating pin.
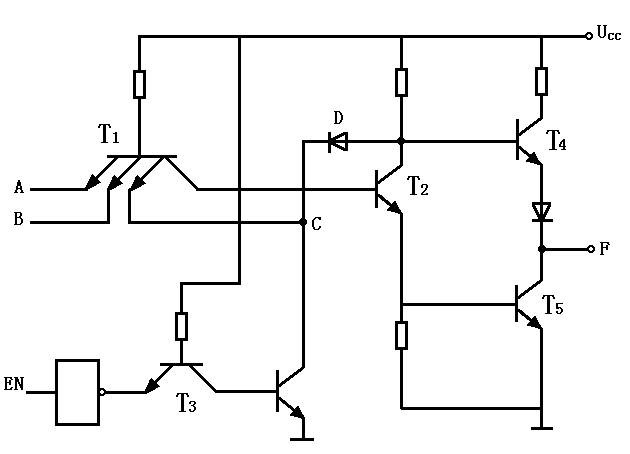
The meaning of the high-resistance state becomes clear when we consider how gate circuits operate. When the pull-up transistor is on and the pull-down transistor is off, the output is at a high level. Conversely, if the pull-up is off and the pull-down is on, the output is low. However, when both transistors are off, the output is in a high-impedance state, which is essentially "floating." At this point, the output level depends on external factors, and the gate no longer controls the output.
Typical Applications:
1. **Bus Structures**: In bus systems, multiple devices are connected to a single bus. Each device is connected using a high-impedance configuration. When a device isn't using the bus, it automatically releases it, allowing other devices to take control.
2. **Microcontroller I/O Pins**: Most microcontrollers allow their I/O pins to be set to high-impedance input mode, such as in the case of Lingyang or AVR microcontrollers. This mode is essentially an infinite input resistance, minimizing any impact on the preceding stage and reducing current flow. It also increases the chip's resistance to voltage surges.
A common representation of the high-impedance state is the letter **Z**.
Tri-State Gate

*Figure 1: Three-state gate logic symbol*
A tri-state gate is a logic gate that has three possible output states: high, low, and high-impedance. The high-impedance state acts like a switch that blocks the signal, similar to an open circuit. These gates usually have an enable (EN) signal that controls whether the output is active or in the high-impedance state. Devices that support these three states are known as tristate devices.
In digital systems, 1 and 0 represent true and false, but sometimes a third state is needed. For example, in situations where something is not clearly true or false, the high-impedance state can act as an intermediate state. In this state, the pin has infinite resistance to ground, so its actual voltage level can be determined by external signals.
One key function of the high-impedance state is to allow input ports to read external voltage levels without affecting the circuit. It effectively isolates the pin from the internal circuitry, making it ideal for applications like bus communication.
The high-impedance state is essentially a way to disconnect a gate from the rest of the circuit. Since physical disconnection isn't always possible, this state simulates it by setting the output to a high resistance. A tri-state gate serves as both a logic extension and a control switch, especially useful in bus systems where only one device should be active at a time.
When connecting a device to a shared bus, a tri-state buffer is required. Only one device can drive the bus at a time, while others must remain in a high-impedance state to avoid conflicts. Bus management ensures that the correct device is enabled, allowing data to be transmitted without interference.
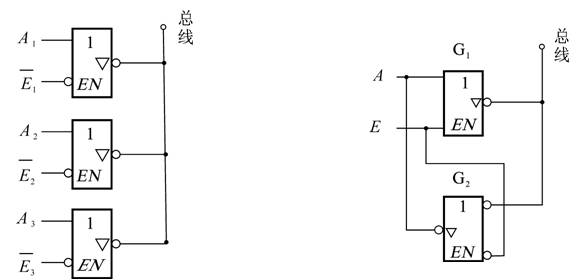
*Figure 2: Three-state gate used in a one-way bus system*
This approach is essential for efficient and safe communication between multiple devices on a shared line. Without tri-state gates, signal collisions could occur, leading to data corruption or damage to components.
Explosion Proof Motor,Explosion Proof Servo Motor,Exproof Motors,Explosion Proof Ac Motor
Yizheng Beide Material Co., Ltd. , https://www.beidevendor.com
