As the level of intelligence increases, more and more robotic sensors are used. There are three types of intelligent robots: interactive robots, sensor robots and autonomous robots. From the anthropomorphic function, vision, force and touch are the most important. It has already entered the practical stage, and the hearing has also made great progress. Others have sense of smell, taste, and slid. There are various sensors, so the robot sensing industry has also formed. Production and research strength.
Internal sensor
Machine-mechatronics products, internal sensors and mechanical parts such as motors and shafts or mechanical structures such as arm (arm), wrist (Wrist), etc. are installed together to complete the measurement of position, speed and strength to achieve servo control.
Position (displacement) sensor
The linear motion sensor has two types of potentiometer sensors and adjustable transformers. The angular displacement sensor has three types: a potentiometer type, a variable transformer (resolver) and a photoelectric encoder. The photoelectric encoder has an incremental encoder and an absolute encoder. The incremental encoder is generally used for zero-position uncertain position servo control. The absolute encoder can obtain the instantaneous value of the drive shaft corresponding to the initial lock position of the encoder. When the device is under pressure, just read each joint code. The reading of the servo can adjust the given value of the servo control to prevent excessive movement during the start of the robot.

Speed ​​and acceleration sensor
Speed ​​sensors measure both translational and rotational motion speeds, but in most cases, they are limited to measuring rotational speed. Using the derivative of the displacement, especially the photoelectric method, the light is irradiated to the rotating disk, and the rotation frequency and the number of pulses are detected to obtain the rotation angle, and the disk is made to have a slit, and the angular velocity is recognized by the two photodiodes, that is, the rotation speed. This is the photoelectric pulse speed sensor. In addition, tachogenerators are used for speed measurement.
A strain gauge, a telescopic gauge, is also a stress sensor for acceleration measurements. The acceleration sensor is used to measure the dynamic control signals of industrial robots. Generally, there is a power derived from the velocity measurement and the power generated by the acceleration of the known mass object, that is, the strain gauge is used to measure the force for deduction, and the following method is also performed:
The force associated with the measured acceleration can be generated by a known mass. This force can be electromagnetic or electrodynamic, and is ultimately reduced to the measurement of the current. This is the servo return sensor, and there are actually many vibrating acceleration sensors.
Force sensor
The force sensor is used to measure the three components of the force between the two objects and the three components of the moment. The ideal sensor in a robot is a semiconductor strain gauge bonded to the compliant component. Specifically, there are a metal resistance type force sensor, a semiconductor type force sensor, other magnetic pressure type, and a force sensor manufactured by the principle of string vibration.
There are also torque sensors (such as the use of photoelectric sensors to measure torque), wrist force sensors (such as the International Stanford Research Institute consists of six small differential transformers, can measure the power in the three directions of the wrist X, Y and Z and Each axis dynamic torque).
Due to the long history of robot development, AC servo systems based on AC permanent magnet motors have been widely used in recent years. Sensors for position and speed are widely used: various types of photoelectric encoders, magnetic encoders and resolvers.
External sensor
In the past, general industrial robots have no external sensory ability, and new generation robots, such as multi-joint robots, especially mobile robots and intelligent robots, require the ability to correct and respond to environmental changes. External sensors are capable of achieving these capabilities.
Tactile sensor
Microswitches are the most common type of contact sensors, as well as isolated two-state contact sensors (ie, bistable switching semiconductor circuits), single analog sensors, matrix sensors (matrix sensors for piezoelectric elements, artificial skin - variable conductivity polymers) , light reflection tactile sensor, etc.).
Stress sensor
For example, when the multi-joint robot is moving, it is necessary to know the actual contact, the position of the contact point (positioning), and the characteristics of the contact, that is, the estimated force (characteristic). Therefore, the strain gauges indicated in the previous section are combined with the specific conditions. The basic assumptions of stress detection, such as the determination of the force between the work surface and the object, specifically the installation of sensors for the environment, the installation of test equipment transmission device for the wrist of the robot as a sensor.
Proximity sensor
Since the movement speed of the robot is increased and the loading and unloading of the object may cause damage, etc., it is necessary to know the a priori information of the position of the object in the robot working site and the appropriate trajectory planning, so it is necessary to apply the remote sensing method of measuring the proximity. Proximity sensors are divided into passive and active sensors, so in addition to natural sources, transmitters and receivers of artificial signals may be required.
An ultrasonic proximity sensor is used to detect the presence and measurement distance of an object. It can't be used to measure distances less than 30~50cm, and the range is large. It can be used on mobile robots or on the handles of large robots. It can also be made into an ultrasound navigation system.
The infrared proximity sensor, which is small in size and only a few cubic centimeters in size, can be mounted on the robotic gripper.
Acoustic sensor
Used to sense and interpret sound waves in a gas (non-contact sensation), liquid or solid (contact sensation). The sonic sensor complexity can range from simple sound wave detection to complex acoustic frequency analysis until individual speech and vocabulary recognition in continuous natural language.
Contact or non-contact temperature sensor
In recent years, it has been widely used in robots. In addition to commonly used thermal resistors (thermistors), thermocouples, etc., thermoelectric TV cameras have also made progress in measuring and sensing temperature images.
Sliding sensor
Used to detect the sliding of an object. When the robot is required to grasp an object of unknown characteristics, it is necessary to determine the most appropriate grip strength value, so it is required to detect the slip signal of the object generated when the grip strength is insufficient.
There are currently a sliding sensor using an optical system and a sliding sensor using a crystal receiver whose detection sensitivity is independent of the sliding direction.
distance sensor
Distance sensors for intelligent mobile robots include laser range finder (which can also measure angles) and sonar sensors, which have been developed in recent years.
Vision sensor
This is a widely used external sensor. In view of its rich content, and machine vision often forms products independently, it has a close relationship with software technology.
HANMAC is specialized in carbon steel weld neck flange, a 105 weld neck flange, As a suppliers/factory, HANMAC wholesale high-quality products of wn flange, class 150 weld neck flange, sch 40 wn flange. we have the perfect after-sales service and technical support. Look forward to your cooperation!
ANSI B16.5 150LBS Weld Neck carbon steel pipeflanges
Product Range:
1.Welding neck Flange 2.Slip on
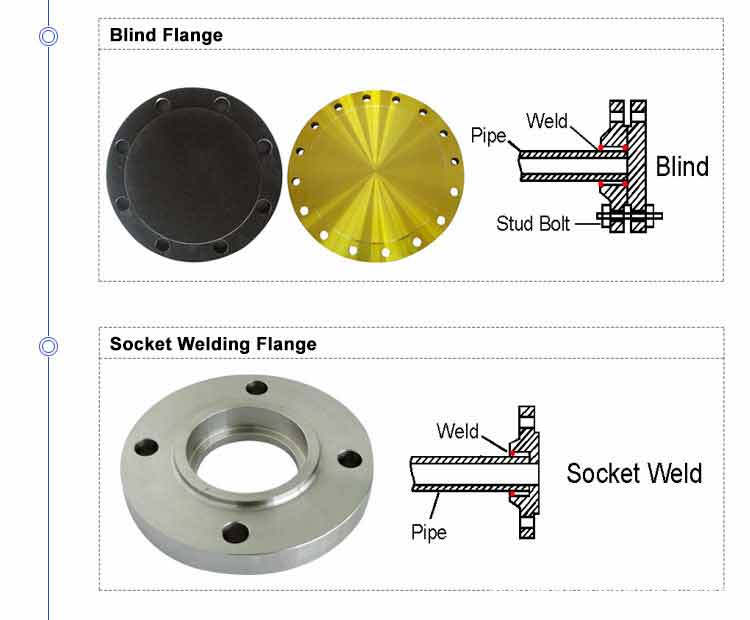
3.Blind Flange 4.Long welding neck flange
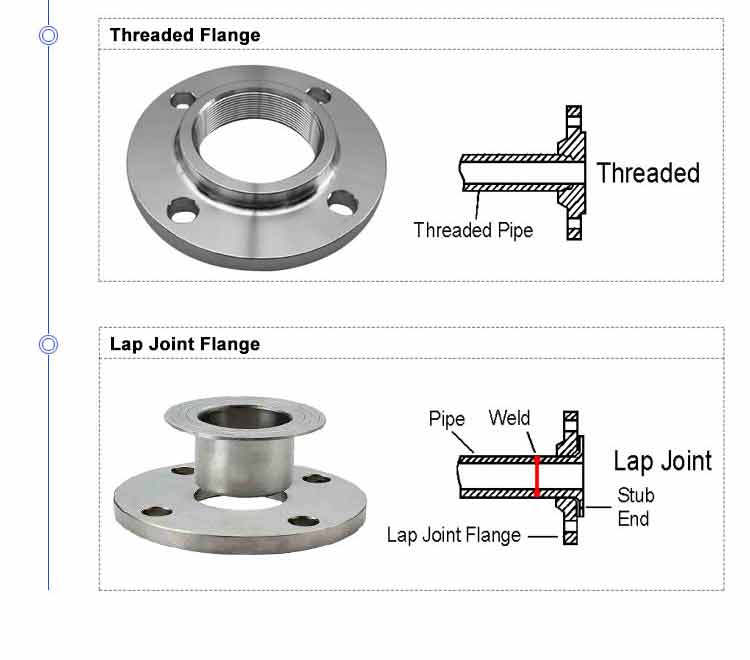
5.Lap joint flange 6.Socket welding
7.Threaded Flange 8.Flat flange
Size:
DN15-DN2000
Pressure:
150#, 300#, 600#,900#,1500#, 2500#
PN6, PN10, PN16, PN25, PN40, PN64, PN100
PN6, PN10, PN16, PN25, PN40
1K, 2K, 5K, 10K, 16K, 20K, 30K, 40K
Standard:
ASME B16.5, ASME B16.47A, ASME B16.47B
BS4504
DIN2631, 2632,2633,2634,2635; DIN2573,2576,2502,2503, 2543,2545;DIN 2527;DIN2565,2566,2567, 2567
GOST12821-80;GOST12820-80
EN1092-1
JIS B2220
Material:
ASTM A105. CS/SA 105/SA105N; CS RST37.2, S235JR; Q235; CS CT20; CS SS400, SF440; S235JRG2,P245GH,P250GH, P280GHM 16MN, 20MN ,20#
Coating:
Black, Yellow paint; rust-proof oil; Antirust oil, Clear lacquer, Black lacquer, Yellow lacquer, Hot-dipped Galvanized, Electrical galvanized
Package:
Ply-Wooden Case for small size
Pallet for big size
Certificate:
TUV,ISO9001:2008;PED97/23/EC,ISO14001:2004,
OHSAS18001:2007
The Third Part Inspection:
BV,SGS,LOIYD,TUV,and other party alloyed by clients
Heat Treatment:
Normalizing, Annealing, Quenching+Tempering
Technical:
forging
Brand
CHM
Min Order:
1PCS
Payment Terms:
T/T, 100% LC AT SIGHT, 100% LC 30 OR 60DAYS AFTER BL OF DATE,
Delivery Time:
7-30days according to acutal order.
Delivery Port:
TIANJIN, QINGDAO,SHANGHAI, NINGBO, SHENZHEN,
Delivery Ability:
500TONS/MONTH
Applicating:
Paper-marking, Oil and natural gas pipeline, Boiler and heat exchanger, Smelting, Water conservancy, Electric power, Chemical,
Pharmaceuticals etc







Carbon Steel Weld Neck Flange, A 105 Weld Neck Flange, PN 16 WN Flange, Class 150 Weld Neck Flange, SCH 40 Wn Flange
HEBEI HANMAC MACHINE CO., LTD. , https://www.chinahanmac.com
