I. Project Overview
This article refers to the address: http://
1.1 Introduction
Nowadays, the energy crisis is getting worse. People's awareness of environmental protection is constantly improving. While developing new energy sources, efforts to improve energy efficiency are also a direction. At present, semiconductor thermoelectric power generation technology has attracted more and more attention with its various advantages. This technology has been applied to industrial waste heat, waste heat recycling, aerospace auxiliary power systems.
During the working process of the notebook computer, the high-speed operation of its CPU and other components will generate a lot of heat. Moreover, with the gradual upgrade of the current hardware configuration of the notebook computer, the overall heat generation of the notebook computer is also increasing while improving the performance. . In order to solve this problem, people have designed a cooling base. However, most of the laptop coolers seen on the market are connected to a laptop via a USB port, or powered by a battery. However, no one has ever designed to use computer waste heat to power it.
This solution intends to develop a notebook computer heat sink powered by computer waste heat using an evaluation kit based on the AVR32 AT32UC3A microcontroller controller and the development system EVK1100.
Second, the demand analysis
2.1 Functional requirements
1. Apply semiconductor temperature difference power generation technology, use computer waste heat to provide the radiator with the energy needed for normal operation.
2. The heat sink has superior heat dissipation effect, low noise, small vibration and more stable operation.
3. The shape design of the radiator is innovative.
2.2 Performance requirements
1. The power supply voltage is stable and the utilization rate of waste heat is high.
2, the use of closed-loop control can be very self-intelligent adjustment, anti-interference ability.
3. The radiator has low noise, small vibration, stable operation and beautiful appearance.
Third, the program design
3.1 System function realization principle

The system contacts the high temperature surface of the temperature difference voltage sheet TEG162 and the computer heat source, and controls the temperature of the low temperature surface by the air flow at the low temperature surface of the TEG162 through the heat sink, thereby controlling the temperature difference within a preset range. We use laptop waste heat to convert it into electricity, and then store it in a lithium battery through a voltage regulator circuit. The stored energy provides an energy source for the entire circuit, eliminating the need to separately power the circuit. In this way, on the one hand, the temperature of the notebook computer can be maintained not too high, and on the other hand, the waste heat recovery of the notebook computer is realized.
Bessel effect: In 1821, the German scientist Saybel discovered the connection between two different metals. If the junction of the connection is placed in the high temperature state T2 (hot end) and the other end is open and in the low temperature state T1 At the cold end, there is an open circuit voltage ΔV at the cold end. This phenomenon is called the Saybol effect. The Seebeck voltage ΔV is proportional to the temperature difference ΔT between the hot and cold ends, ie ΔV=kΔT=k(T2-T1), where k It is the Seebeck parameter, which is determined by the electronic band structure of the material itself.
From ΔV=kΔT=k(T2-T1), when the notebook CPU temperature is within the range of 50-60 degrees under normal conditions, the ambient temperature varies from 0 to 10 degrees depending on the season, and ΔV=kΔT=k(T2) - T1), the average temperature difference voltage in a year range is 4 to 5V, the current is 600mA, and the average power P = U × I, which is about 2.4-3W. If after 5 years, the energy recovered by a computer is about 131.4 degrees, how many laptops does the world have? So this is a big part of the energy. This shows that the program is highly feasible.
TEG162 basic information:
Electrical parameters: When the temperature difference is 120 °C, the open circuit voltage is 17V, the short circuit current is 1A, the load voltage is 12V, and the load current is 600MA.
Size: 62 × 62 × 3.8
Years of use: 5 years or so
3.2 Hardware platform selection and resource configuration
The evaluation module of the AVR32 AT32UC3A microcontroller controller and the temperature module on the development system EVK1100 monitor the temperature of the laptop in real time and transmit the temperature signal to the AT32UC3A for processing, so that the temperature of the notebook computer only changes within the safe range.
3.3 System Software Architecture and Software Process
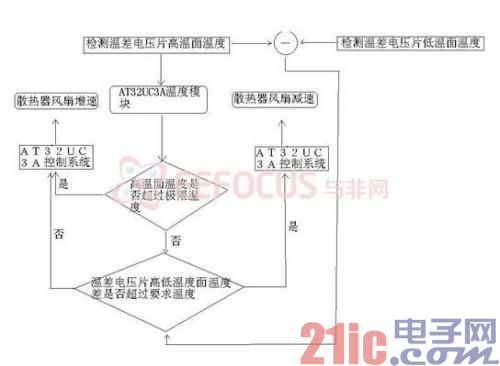
The temperature module on the AT32UC3A development board collects the temperature of the notebook in real time, and controls the rotation speed of the radiator fan by comparing with the preset temperature, so that the temperature of the notebook computer changes within the normal range.
3.4 System Expected Results
1. Realize the recycling and storage of waste heat energy of notebook computers.
2. Realize that the stored energy of the laptop can work normally without increasing the external power supply, and also ensure that the laptop is not too high and the hardware is damaged.
I. Project Overview
1.1 Introduction
Nowadays, the energy crisis is getting worse. People's awareness of environmental protection is constantly improving. While developing new energy sources, efforts to improve energy efficiency are also a direction. At present, semiconductor thermoelectric power generation technology has attracted more and more attention with its various advantages. This technology has been applied to industrial waste heat, waste heat recycling, aerospace auxiliary power systems.
During the working process of the notebook computer, the high-speed operation of its CPU and other components will generate a lot of heat. Moreover, with the gradual upgrade of the current hardware configuration of the notebook computer, the overall heat generation of the notebook computer is also increasing while improving the performance. . In order to solve this problem, people have designed a cooling base. However, most of the laptop coolers seen on the market are connected to a laptop via a USB port, or powered by a battery. However, no one has ever designed to use computer waste heat to power it.
This solution intends to develop a notebook computer heat sink powered by computer waste heat using an evaluation kit based on the AVR32 AT32UC3A microcontroller controller and the development system EVK1100.
Second, the demand analysis
2.1 Functional requirements
1. Apply semiconductor temperature difference power generation technology, use computer waste heat to provide the radiator with the energy needed for normal operation.
2. The heat sink has superior heat dissipation effect, low noise, small vibration and more stable operation.
3. The shape design of the radiator is innovative.
2.2 Performance requirements
1. The power supply voltage is stable and the utilization rate of waste heat is high.
2, the use of closed-loop control can be very self-intelligent adjustment, anti-interference ability.
3. The radiator has low noise, small vibration, stable operation and beautiful appearance.
Third, the program design
3.1 System function realization principle

The system contacts the high temperature surface of the temperature difference voltage sheet TEG162 and the computer heat source, and controls the temperature of the low temperature surface by the air flow at the low temperature surface of the TEG162 through the heat sink, thereby controlling the temperature difference within a preset range. We use laptop waste heat to convert it into electricity, and then store it in a lithium battery through a voltage regulator circuit. The stored energy provides an energy source for the entire circuit, eliminating the need to separately power the circuit. In this way, on the one hand, the temperature of the notebook computer can be maintained not too high, and on the other hand, the waste heat recovery of the notebook computer is realized.
Bessel effect: In 1821, the German scientist Saybel discovered the connection between two different metals. If the junction of the connection is placed in the high temperature state T2 (hot end) and the other end is open and in the low temperature state T1 At the cold end, there is an open circuit voltage ΔV at the cold end. This phenomenon is called the Saybol effect. The Seebeck voltage ΔV is proportional to the temperature difference ΔT between the hot and cold ends, ie ΔV=kΔT=k(T2-T1), where k It is the Seebeck parameter, which is determined by the electronic band structure of the material itself.
From ΔV=kΔT=k(T2-T1), when the notebook CPU temperature is within the range of 50-60 degrees under normal conditions, the ambient temperature varies from 0 to 10 degrees depending on the season, and ΔV=kΔT=k(T2) - T1), the average temperature difference voltage in a year range is 4 to 5V, the current is 600mA, and the average power P = U × I, which is about 2.4-3W. If after 5 years, the energy recovered by a computer is about 131.4 degrees, how many laptops does the world have? So this is a big part of the energy. This shows that the program is highly feasible.
TEG162 basic information:
Electrical parameters: When the temperature difference is 120 °C, the open circuit voltage is 17V, the short circuit current is 1A, the load voltage is 12V, and the load current is 600MA.
Size: 62 × 62 × 3.8
Years of use: 5 years or so
3.2 Hardware platform selection and resource configuration
The evaluation module of the AVR32 AT32UC3A microcontroller controller and the temperature module on the development system EVK1100 monitor the temperature of the laptop in real time and transmit the temperature signal to the AT32UC3A for processing, so that the temperature of the notebook computer only changes within the safe range.
3.3 System Software Architecture and Software Process

The temperature module on the AT32UC3A development board collects the temperature of the notebook in real time, and controls the rotation speed of the radiator fan by comparing with the preset temperature, so that the temperature of the notebook computer changes within the normal range.
3.4 System Expected Results
1. Realize the recycling and storage of waste heat energy of notebook computers.
2. Realize that the stored energy of the laptop can work normally without increasing the external power supply, and also ensure that the laptop is not too high and the hardware is damaged.
35W UGR Downlights,Dimmable LED Downlight,UGR LED Downlight,Recessed LED Downlight
SHENZHEN KEHEI LIGHTING TECHNOLOGY CO.LTD , https://www.keheiled.com
